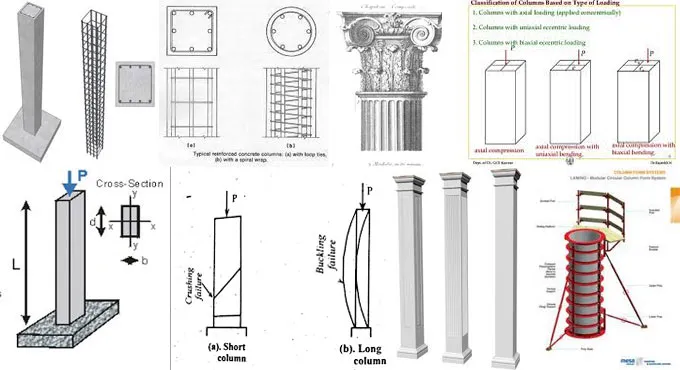
Columns are crucial structural elements in building construction, providing support and stability to the entire structure. They come in various shapes, sizes, and materials, each serving specific purposes based on architectural and engineering requirements. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various types of columns used in building construction.
Classical Columns:
- Doric: The Doric column is one of the oldest and simplest classical columns, characterized by its fluted shaft, plain capital, and lack of a base. It is commonly found in ancient Greek and Roman architecture.
- Ionic: Ionic columns feature distinctive spiral scrolls or volutes on their capitals. They are more ornate than Doric columns and are often seen in Greek temples.
- Corinthian: Corinthian columns are the most ornate of the classical orders, with intricately designed capitals adorned with acanthus leaves. They are often used in grand and decorative buildings.
Modern Columns:
- Reinforced Concrete Columns: These columns are made of concrete and reinforced with steel bars or mesh to enhance their load-bearing capacity. They are widely used in modern construction due to their strength and versatility.
- Steel Columns: Steel columns are fabricate from structural steel and are commonly use in high-rise buildings and industrial structures due to their exceptional strength-to-weight ratio.
- Wooden Columns: Wooden columns, typically made from timber, are use in traditional and residential construction. They provide a warm and rustic aesthetic and can be ornately carve for decorative purposes.
A Based on Shape:
- Rectangular Columns: These columns have a rectangular cross-section and are often use in buildings where space constraints or architectural preferences dictate a specific shape.
- Circular Columns: Circular columns are cylindrical in shape and are often prefer for their aesthetic appeal and load-bearing capacity.
- Square Columns: Square columns have a square cross-section and are commonly use in both traditional and modern construction.
Based on Load-Bearing Capacity:
- Axially Loaded Columns: These columns primarily bear axial loads, such as the weight of the floors and roof. They are designe to withstand compression forces.
- Eccentrically Loaded Columns: Eccentrically loaded columns experience both axial and lateral forces. Special design considerations are require to account for the off-center loads.
A Based on Structural System:
- Interior Columns: These columns are located within the interior of the building and are not typically visible from the exterior.
- Exterior Columns: Exterior columns are part of the building’s façade and are often more decorative and visually prominent.
Based on Material Finish:
- Clad Columns: These columns are cover with decorative materials like stone, marble, or tile to enhance their appearance.
- Exposed Columns: Expose columns are left with their natural finish, often showcasing the material use, such as concrete or steel.
Specialty Columns:
- Pilasters: Pilasters are shallow, rectangular columns attached to walls for decorative purposes and to create the appearance of structural support.
- Composite Columns: Composite columns combine elements of different classical orders, such as Ionic and Corinthian, to create unique designs.
- Load-Bearing Columns: These columns are specifically designe to carry heavy loads and are common in industrial buildings and infrastructure projects.
Column Bases and Capitals:
- The base is the bottom part of the column that rests on the foundation.
- The capital is the topmost part of the column that supports the load from above and provides architectural detail.
In conclusion, columns are essential components of building construction, serving both structural and architectural purposes. The choice of column type depends on factors like architectural style, structural requirements, and material preferences. Proper design and construction of columns are crucial to ensure the safety and longevity of a building.